Design Technology
What is the intent of our Design Technology Curriculum?
Design Technology aims for all students to develop an understanding of problem solving and using their creativity. It is an area of study that focuses on researching, planning, designing, creating products, and forming evaluations on the success of the outcome.
Design Technology is a creative and practical subject which allows students to be imaginative in a range of skill areas from Electronics, Textiles, Resistant Materials, Graphics, CAD/CAM, and Systems. Students will make products in a variety of materials, developing a varied practical skill base which they are able to actively use in the Academy and at home.
The aim of the Design Technology department is to develop student’s knowledge and understanding of a wide variety of skills including practical skills in multiple mediums, theoretical learning of materials, manufacturing and designing. Design Technology is a subject which fosters student’s creativity and independence and allows students to make products in different material mediums. Design Technology is a popular subject in which students are be able to expand their creativity, problem solving, planning, and evaluation skills as well as communication and teamwork skills.
Co-curricular and Enrichment opportunities
- GCSE Support Sessions for NEA
- IB Support Sessions for IA and Revision
- Soapbox Challenge
- Young Engineers Project
Useful websites
Years 7, 8 & 9
MYP Design is the link between innovation and creativity, taking thoughts and exploring the possibilities, allowing products to be redefined and through prototyping, experimentation, and adaptation. Designing requires an individual to be imaginative and creative, while having a knowledge base that will aid the process and need to be supported by appropriate research and investigation. Design is human-centred and focuses on the needs, wants and limitations of the end user. The use of well-established design principles and processes increases the marketability that a design will be successful. To do this, designers use a wide variety of principles which, taken together, make up what is known as the design cycle. MYP design challenges all students to apply practical and creative thinking skills to solve design problems; encourages students to explore the role of design in both historical and contemporary contexts; and raises students’ awareness of their responsibilities when making design decisions. The aims of MYP design are to encourage and enable students to:
- enjoy the design process, develop an appreciation of its elegance and power.
- develop knowledge, understanding and skills from different disciplines to design and create solutions to problems using the design cycle.
- use and apply technology effectively as a means to access, process and communicate information, model and create solutions, and to solve problems.
- develop an appreciation of the impact of design innovations for life, global society and environments.
- appreciate past, present and emerging design within cultural, political, social, historical and environmental contexts.
- develop respect for others’ viewpoints and appreciate alternative solutions to problems.
- act with integrity and honesty and take responsibility for their own actions developing effective working practices.
Criterion A: Inquiring and Analysing
- Students are presented with a design situation, from which they identify a problem that needs to be solved. They analyse the need for a solution and conduct an inquiry into the nature of the problem.
- explain and justify the need for a solution to a problem for a specified client/target audience.
- identify and prioritize the primary and secondary research needed to develop a solution to the problem.
- analyse a range of existing products that inspire a solution to the problem.
- develop a detailed design brief which summarizes the analysis of relevant research.
Criterion B: Developing Ideas
- Students write a detailed specification, which drives the development of a solution. They present the solution.
- develop a design specification which clearly states the success criteria for the design of a solution.
- develop a range of feasible design ideas which can be correctly interpreted by others.
- present the final chosen design and justify its selection.
- develop accurate and detailed planning drawings/diagrams and outline the requirements for the creation of the chosen solution.
Criterion C: Creating the Solution
- Students plan the creation of the chosen solution and follow the plan to create a prototype sufficient for testing and evaluation.
- construct a logical plan, which describes the efficient use of time and resources, sufficient for peers to be able to follow to create the solution.
- demonstrate excellent technical skills when making the solution.
- follow the plan to create the solution, which functions as intended.
- fully justify changes made to the chosen design and plan when making the solution.
Criterion D: Evaluating
- Students design tests to evaluate the solution, carry out those tests and objectively evaluate its success. Students identify areas where the solution could be improved and explain how their solution will impact on the client or target audience.
- design detailed and relevant testing methods, which generate data, to measure the success of the solution.
- critically evaluate the success of the solution against the design specification
- explain how the solution could be improved.
- explain the impact of the solution on the client/target audience.
For further information, click here.
Year 7
- Understanding and applying health and safety practices in the workshop
- Understanding the key words used in Design and Technology
- Understanding designing products for function and form
- Learning about the different materials in Textiles, Resistant Materials, Graphics and CAD/CAM and their working properties
- Learning about the sources and origins of different materials in Textiles, Resistant Materials, Graphics and CAD/CAM
- Students will be able to identify the different materials in Design and Technology
- Student will be able to demonstrate a range of making and finishing skills using different construction processes, surfaces and finishes.
- Students will be able to adapt and follow demonstrations, using materials and equipment to prepare and create a range of products.
- Students will be able to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the above concepts, when designing, planning, and evaluating products
Examples Of Practical Work:
- Textiles Scrap Monster project
- Photo Frame
- Metal Magnet
- Table Tennis Paddle
Year 8
- Understanding designing products using new and emerging technologies
- Learning about the systems required to make products effectively in different materials in Textiles, Resistant Materials, Graphics and CAD/CAM
- Learning about the communication of design ideas and focusing on creating more sustainable products
- Students will continue to apply and develop the principles of health and safety in Design and Technology
- Students to learn and create products using more advanced construction processes involving equipment and machinery building on the skills acquired in Year 7
- Students are able to recall and apply the key words, sources and origins, different materials and their working properties.
- Students to demonstrate a wider range of making and finishing skills to create more complex products.
Examples Of Practical Work:
- Night light
- Passive amplifier
- Graphics
- Child’s Mobile
Year 9
- Understand the use of tolerances to make products to a high quality.
- Learning about skills to make products using mechanical and electronic systems in different materials in Textiles, Resistant Materials, Graphics and CAD/CAM
- Learning about the design cycle to complete the iterative design process.
- Students will continue to apply and develop the principles of health and safety in Design and Technology independently whilst making unique products.
- Students to learn and create products using multi-media construction processes involving equipment and machinery building on the skills acquired in Year 8
- Students are able to recall and apply the key words, sources and origins, different materials and their working properties from Year 7 and the communication of design ideas, systems and new and emerging technology from Year 8
- Students to demonstrate a complex range of making and finishing skills to create more complex products.
Examples Of Practical Work:
- Mechanical Toy
Years 10 & 11
Course Title: Design and Technology (8552 )
Exam Board: AQA
Qualification: GCSE
About the course
The GCSE Design and Technology qualification is modern and relevant, which students can learn about contemporary technologies, materials and processes, as well as established practices in the subject which form part of the examination. There is emphasis on understanding and applying iterative design processes which form part of the Non-Examined Assessment. Students will use their creativity and imagination to design and make prototypes that solve real and relevant problems, considering their own and others’ needs, wants, and values.
For GCSE Design and Technology students should:
- develop realistic design proposals because of the exploration of design opportunities and users’ needs, wants and values.
- use imagination, experimentation and combine ideas when designing.
- develop the skills to critique and refine their own ideas whilst designing and making.
- communicate their design ideas and decisions using different media and techniques, as appropriate for different audiences at key points in their designing.
- develop a broad knowledge of materials, components and technologies and practical skills to develop high quality, imaginative and functional prototypes.
- demonstrate safe working practices in design and technology.
Course Content
50% Written exam consisting of one paper. Paper 1 is a 2hour examination which is worth 100 marks which students core technical, specialist technical, designing and making principles are assessed in three sections.
Section A – Core technical principles (20 marks) A mixture of multiple choice and short answer questions assessing a breadth of technical knowledge and understanding.
Section B – Specialist technical principles (30 marks) Several short answer questions (2–5 marks) and one extended response to assess a more in-depth knowledge of technical principles.
Section C – Designing and making principles (50 marks) A mixture of short answer and extended response questions.
50% Non-Examined Assessment consisting of design portfolio and physical product made by the student. The NEA project is decided by the student in response to contents given by the exam board and focuses on using the design process to create a product for the commercial market. The project takes approximately 30 to 35 hours and worth 100 marks which students are assessed in the practical application of core technical, specialist technical, designing and making principles are assessed in six sections.
Section A: Identifying and investigating design possibilities
Section B: Producing a design brief and specification
Section C: Generating design ideas
Section D: Developing design ideas
Section E: Realising design ideas
Section F: Analysing & evaluating.
For further information, click here.
Year 10
Students will continue to build their knowledge in Design and Technology that they have gained through Key Stage 3. Students will be able to understand the GCSE requirements of design and technology as they will practise a mini-NEA project and carry out many practical tasks to embed their making skills as well as developing a knowledge and understanding of the theoretical elements for the examination
Examples of Practical Work in Year 10
- Product of their choice from investigation, design and planning in the practise a NEA project. Students choose the materials that this product will be made from.
- Skills based practical sessions in different materials link to theoretical practice.
Year 11
Students will complete their NEA which is 50% of their final grade for their GCSE in Design and Technology and continue with revision for preparation of the summer examination.
Useful Websites
Years 12 & 13
Course Title: Engineering (Level 3 / National / Extended Certificate)
Exam Board: Pearsons
Qualification: BTEC Engineering
Key Opportunities
- We provide students with challenging opportunities through the process of working as part of a team to design, plan and produce an engineered product.
- We cover industry standard Computer Aided Design and Manufacture (CAD/CAM) which enables students to actively engage and take responsibility for their personal development in the process of engineering design to develop as effective and independent life-long learners.
- Students will learn to make decisions, consider sustainability, and combine skills with understanding to design and make engineered products, exploring ways in which technical, economic, and environmental, factors interact to shape designing and making.
- Students will develop an understanding of why analysing existing products will help produce practical solutions to needs.
- Students will understand the manufacturing process and they can design new and improved products which have an impact on technical capability, efficiency, environmental impact, and safety factors.
- The vast nature of disciplines and knowledge which come under the umbrella of Engineering, provide endless opportunities for a wide variety of employment and higher education possibilities.
Student Skill Development
This course develops pupils’ real skills, inspires, and motivates, and helps them to prepare for the future and to take the next step towards an engineering education and/or career adventure.
-
Engineering is defined as “the profitable application of science, maths and technology.” In other terms, engineers make products and processes work, and keep them working, in an affordable way.
-
We are all in some small way ‘engineers’, what this subject does is to foster and enhance that inherent talent by allowing students to achieve in the knowledge, tools, skills, and expertise and to practice and develop that skill set and to apply it to increasingly challenging situations.
-
We will aim to provide Community Involvement: Visiting speakers to discuss their business interest in Engineering. Ex-students following either apprenticeships and/or university courses.
-
The course specification claims that: “This qualification provides a broad basis of study for the engineering sector. It has been designed to support progression to higher education when taken as part of a programme of study that includes other appropriate BTEC Nationals or A Levels.”
-
This is a theory and practice-based course:
-
The course combines theoretical content with practical application.
-
The use of mathematical skills is a key requirement and is tested in the examination.
-
An understanding of underlying scientific principles is expected.
-
An iterative approach to designing is encouraged.
-
The acquisition of practical skills is still expected.
About the course
In engineering we look at developing critical thinking and practical skills and applying scientific and mathematical principles to resolve technical and design situations to provide students with a breadth and depth of knowledge and skills.
Course Content
BTEC Engineering Level 3 (extended certificate) building blocks:
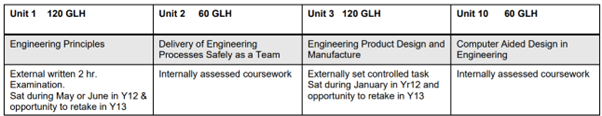
- External assessment: Units 1 and 3 are externally assessed. Each assessment is taken under specified conditions, then marked by Pearson and a grade awarded. Learners are permitted to re-sit external assessments during their programme. You should refer to our Academy’s current policy information on permitted retakes.
- Unit 1: Examinations – all learners take the same assessment at the same time, normally with a written examination paper.
- Unit 3: Set task – learners take the assessment during a defined window and demonstrate understanding through completion of a vocational task. Some external assessments include a period of preparation using set information. This unit will be internally assessed coursework that will then be moderated by BTEC/Pearsons.
- Internal assessment: Two units (units 2 and 10) are internally assessed to external standards verification. This means that a set and assess assignment will provide a report/coursework for each of the two units.
- Students are given opportunities to:
- write up the findings of their own research.
- use case studies to explore complex or unfamiliar situations.
- carry out projects for which they have choice over the direction and outcomes.
- demonstrate practical and technical skills using appropriate processes, devices, components, equipment, materials, consumables. You will make grading decisions based on the requirements and supporting guidance given in the units.
Year 12
Students will cover Unit 1 and Unit 2. Students will prepare for Unit 3, ready for Year 13.
Year 13
Students in their final year of Sixth Form, complete Unit 3 and 10. Students will get an opportunity to resit their external examination for Unit 1 if required.
Useful websites
- https://qualifications.pearson.com/en/qualifications/btec-nationals/engineering-2016.html
- http://www.technologystudent.com/
- http://www.imeche.org/
- https://www.engc.org.uk/
Connections to future pathways Careers
Mechanical technician, Maintenance technician, Production engineer, Automotive engineer, Maintenance engineer, Design engineer, Structural engineer, Aerospace engineer, Crash test investigator, Electrical engineer, Mechanical technician, Manufacturing engineer, Process engineer, Quality Engineer, Technical illustrator, Design documentation officer, CAD Draftsperson, CAD/CAM operator
Future learning
Mechanical Engineering: Transport engineering, Robotics and mechatronics, Production engineering, Electrical engineering, Design engineering, CAD/CAM engineering, Set Designer, CAD draughts person, Quantity Surveyor.







